ETS software
A single manufacturer-independent Engineering Tool Software is used to plan, design and commission KNX installations with KNX-certified products: ETS ®. System integrators can use ETS software for connecting products from different manufacturers and from different application domains to form a single installation.
A KNX installation can be programmed by one of the following two configuration modes:
• Easy Mode (E-Mode)
Here the system is configured not via a PC, but using a handheld unit, push buttons, or other means. This configuration method is suitable for electricians with a basic knowledge of bus technology, but no software skills. S-Mode devices (see below) can still always be added to the installation at a later stage.
• System Mode (S-Mode)
To configure S-Mode devices, a special program – the Engineering Tool Software (ETS) – is needed. ETS can also be used to connect and commission KNX devices.
Functions of ETS software
A KNX installation is typically configured in S-mode, i.e. using a computer with ETS installed on it. ETS software is used for processing the application software that manufacturers supply with their products. It can be used to perform e.g. the following tasks:
• Downloading manufacturers’ application software from the internet (online catalogue) or reading in a manufacturer’s database (e.g. as offered by the manufacturer via his website)
• Setting the parameters for the application software
• Using Group Addresses to link the Group Objects for of the individual Application Programs
• Downloading application software into KNX devices from ETS software
In addition to design and commissioning tools, ETS software also offers extensive assistance with diagnostics and troubleshooting.
ETS program structure
ETS has been created according to Windows design rules, so users who already work with Microsoft ® products will not need long to learn how to use it. ETS software has a number of windows, each representing a KNX installation in a different way:
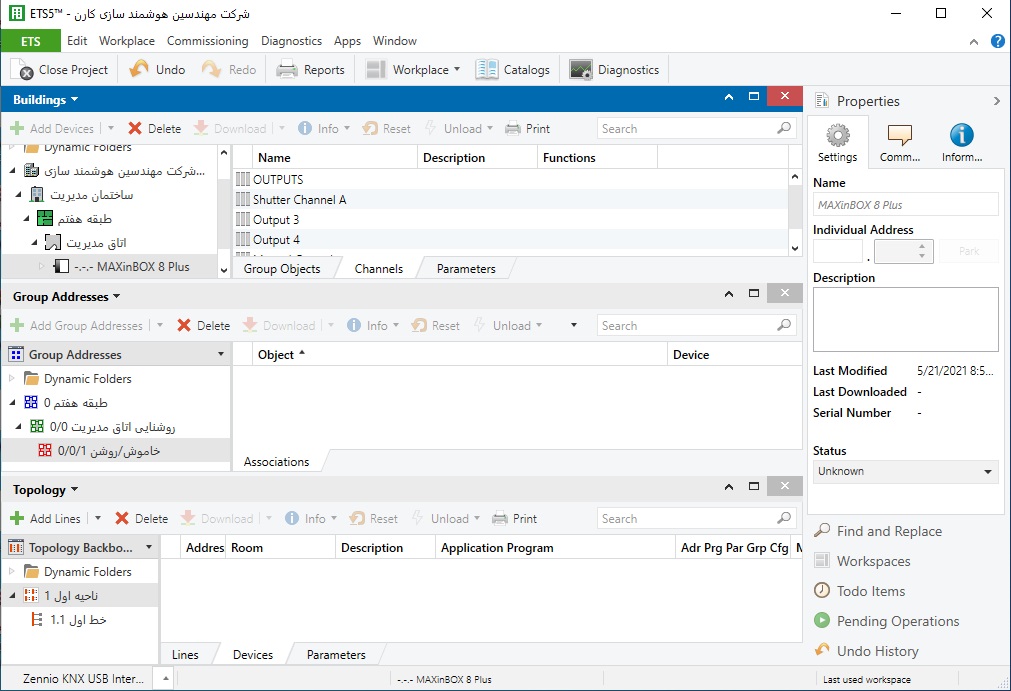
• The main window presents the installation from the point of view of the building, showing its various rooms and distribution boards. Devices can be assigned to individual rooms and distribution boards, making it easy to find a device in ETS on the basis of its location in the building
• The Group Address window shows the KNX installation from the point of view of the functions it offers. Here it is easy to see what devices in the building interact with each other in what way
• The topology window shows the structure (Individual Addresses) of the KNX installation that is being edited.
Each window is divided into two halves, with the left-hand side providing a general overview of the installation in tree form, and the right-hand side presenting in list form individual sections of the tree structure selected in the left-hand part. Along the top edge of the window are menu bars from which individual functions can be called up. There are also toolbars providing quick, simple access to the program’s most popular functions. The user can customize the appearance of the lists in the righthand part of the window and the symbols in the toolbars, to adapt them to his or her personal working style.
Designing a KNX installation
To design a KNX installation, it is not enough to merely install ETS software on a computer. The product data provided by the manufacturers of the various devices also need to be imported into the program. These data are available free-of-charge from manufacturers of KNX products, either online or directly from the manufacturer. They can also be accessed in the ETS Online KNX Product catalogue.
Once these data have been imported into ETS, the design of the installation can commence. This involves the following steps:
• Creating a project with the required data. The project can be later opened and edited again at any time via the attributed project name,
• Depicting the layout of the building and the devices in it ; defining the building structure and bus topology; defining the Individual Addresses of the devices
• Defining the parameters for KNX products as required. In the case of a push button, for example, it is necessary to define whether the push button is to be a dimmer switch, a push-button for controlling blinds, or a simple push button for switching a light on and off. In the case of an actuator, these parameters determine how the actuator behaves, e.g. whether it should offer timer functions or, if it is a dimmer, how quickly the brightness should change from the previous to the new setting
• Defining the functions of the system and the Group Addresses.
Example: in an office there are two strips of lighting that work independently from one another. It should be possible to turn each light on and off individually, but it should also be possible to switch both lights on and off together, so the actuator needs to be programmed with three different functions. Three Group Addresses are therefore needed (strip light 1 on/ off, strip light 2 on/off, and strip lights 1 and 2 on/off)
• Linking the Group Objects of the KNX products via Group Addresses. This is done by connecting “virtual cables” in ETS between the devices’ virtual inputs and outputs. By linking Group Objects in this way, the user can define which sensors control which actuators
• Specifying the trades to which the KNX devices in the installation relate (optional)
• Checking that the installation has been designed correctly, printing documentation, and saving and backing up the project
Commissioning
Commissioning is one of the most important functions of ETS software. Each device first needs to be individually assigned a Individual Addresses, which the ETS user responsible for commissioning the installation does by pressing the programming button on the device; this tells the program that the address next in line to be issued should be assigned to that particular device.
Special care is needed during this stage of the commissioning process, because errors at this point can lead to malfunctions later on, the correction of which can be very time-consuming.
Once all devices have a Individual Addresses, it is time to download the software into them.
Diagnostic functions
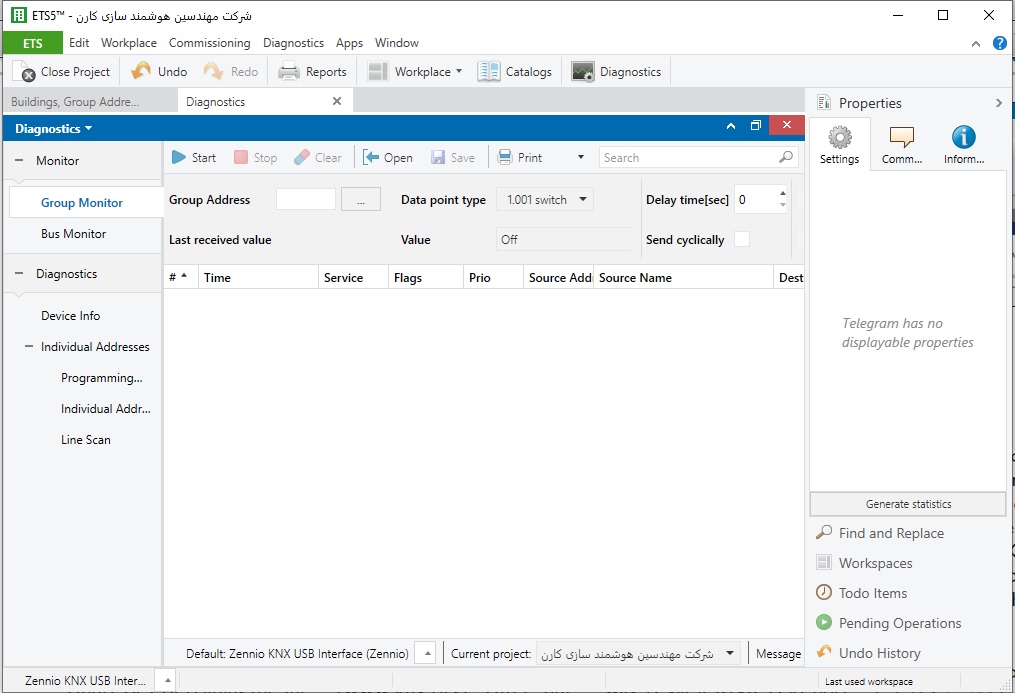
ETS software offers a number of diagnostic functions, for example for checking devices’ Individual Addresses, or reading the status of a given bus device. This includes details of the device’s manufacturer, any error bits in the bus coupling unit, and the operating status of the device.
The operating status indicates whether the software is currently running. It is also possible to see whether there is an appropriate end device connected via the PEI to the bus coupling unit, and what Group Addresses are assigned to the objects of the device.
The bus and group monitor can be used to monitor all bus telegrams and hence observe activity on the bus. This makes it easy to diagnose and locate any errors.
In addition to monitoring telegrams, it is also possible to send telegrams from a computer, and in this way to test actuators and initiate switching operations in the installation without the relevant sensors yet being installed. This is convenient for e.g. testing individual room controls, for example checking that the heating switches off when the windows are open (even though e.g. the relevant window contacts have not yet been fitted).
Installation and licensing
ETS is sold by KNX Association in the KNX Online Shop (www.knx.org). After purchase it can be downloaded directly from the internet, and can be installed on any computer. To work with ETS software, users require a license, of which there are several types available:
Software license for ETS Professional. ETS Professional is the full version of ETS. The software license is only valid for one computer
• Dongle license for ETS Professional A hardware dongle is also required; this is a portable license that can be connected to a USB port on any computer.
Thanks to the dongle, ETS can be used on any computer
• ETS supplementary licenses: up to two further licenses can be bought for a small additional charge. This is particularly convenient for smaller companies
• ETS Lite license: inexpensive ETS software trainee licenses offering limited functionality are available for school pupils and students
Interfaces
For use in commissioning and diagnostics, ETS software needs to be connected to the KNX bus.
There are various ways of achieving this: the standard way is via a KNX USB port or KNXnet/IP interface (or KNXnet/IP router). If the network installation has a Wi-Fi connection, the bus can also be accessed wirelessly from a laptop.
Plug-ins
The configuration and commissioning of some KNX devices requires additional special software. In displays, for example, the page structure, texts that will be shown on the display, and link to events in the bus system are all defined by the person responsible for designing the installation.
For this, a separate software plug-in is typically required. Plug-ins are automatically called up as soon as the user starts editing the device parameters in ETS software.
ETS Apps
Apps are widely available for phones, smartphones and tablets and now for ETS as well. ETS Professional offers generally all that is needed in order to work with a KNX installation. But, like mobile phone users, users of the KNX system also increasingly want access to a wide range of additional functions. By offering Apps for its Engineering Tool Software (ETS software), KNX is responding to growing demand around the world for specialized solutions. Compatible Apps can increase the functions of ETS yet further. They allow KNX experts in particular to enjoy even greater transparency, and configure KNX installations more quickly than ever.
Thanks to the Apps, ETS can be adapted to users’ future wishes and to future technical developments. All Apps are designed by KNX Association and the KNX members. Validated by KNX Association, they are available to purchase from the KNX Online Shop.